Flow Area Example
An example of the FlowArea widget.
A FlowArea is a very powerful tool for creating a flowing layout of
widgets. A FlowArea accepts an arbitrary number of FlowItem children,
each of which holds a Container as its content. The layout of these
FlowItem children is controlled by the FlowArea attributes:
directionThis is an enum controlling how the items are arranged in the area. Allowable values are ‘left_to_right’, ‘right_to_left’, ‘top_to_bottom’, and ‘bottom_to_top’; and indicate the direction in which items will be added to the area. When the layout space in a given direction is exhausted, the layout will wrap around to the next line. With horizontal directions, lines are stacked top to bottom. With vertical directions, lines are stacked left to right.
alignThis is an enum controlling how a layout line is aligned within the layout space. If there is any space leftover after laying out a given line of widgets, that space is distributed according to the value of this enum. Allowable values are ‘leading’, ‘trailing’, ‘center’, and ‘justify’.
horizontal_spacingThis is an int specifying how much horizontal space to place between items or lines in the layout.
vertical_spacingThis is an int specifying how much vertical space to place between items or lines in the layout.
marginsThis is a Box of ints specifying how much margin to place on the outside of the layout.
Each FlowItem used in the layout can further customize the behavior:
preferred_sizeThis is a Size specifying the desired layout size for the item. This size will be used whenever possible, but will not override the minimum or maximum size of the item. If set to (-1, -1) (the default), then the size hint for the item will be used.
alignThis is an enum which controls the orthogonal alignment of the item. When an item has neighbors which are larger than itself in the orhthongonal direction, this value controls how the item aligns within that additional space. The valid values area ‘leading’, ‘trailing’, and ‘center’.
stretchThis is an int which controls the amount that the widget should expand to take up additional space in the layout direction. The default is 0 and means that the widget will not expand. When the value is greater than zero, the value is weighted against the stretch factors of the other items in the same line to determine the amount of space given to the item.
ortho_stretchThis is an int which controls the amount that the widget should expand to take up additional space orthogonal to the layout direction. The default is 0 and means that the widget will not expand. If no item in a given line can expand in the ortho direction, then the line will not expand. Otherwise, the stretch factor for a line is equivalent to the maximum of the ortho stretch factors for all items in the line. The extra orthogonal space is then proportioned to the lines weighted on this stretch factor.
The code below creates a flow area populated with several initial flow items. Items can be added and removed, and each individual item is configurable. There is a single item which cannot be removed, and which controls the parameters for the entire area.
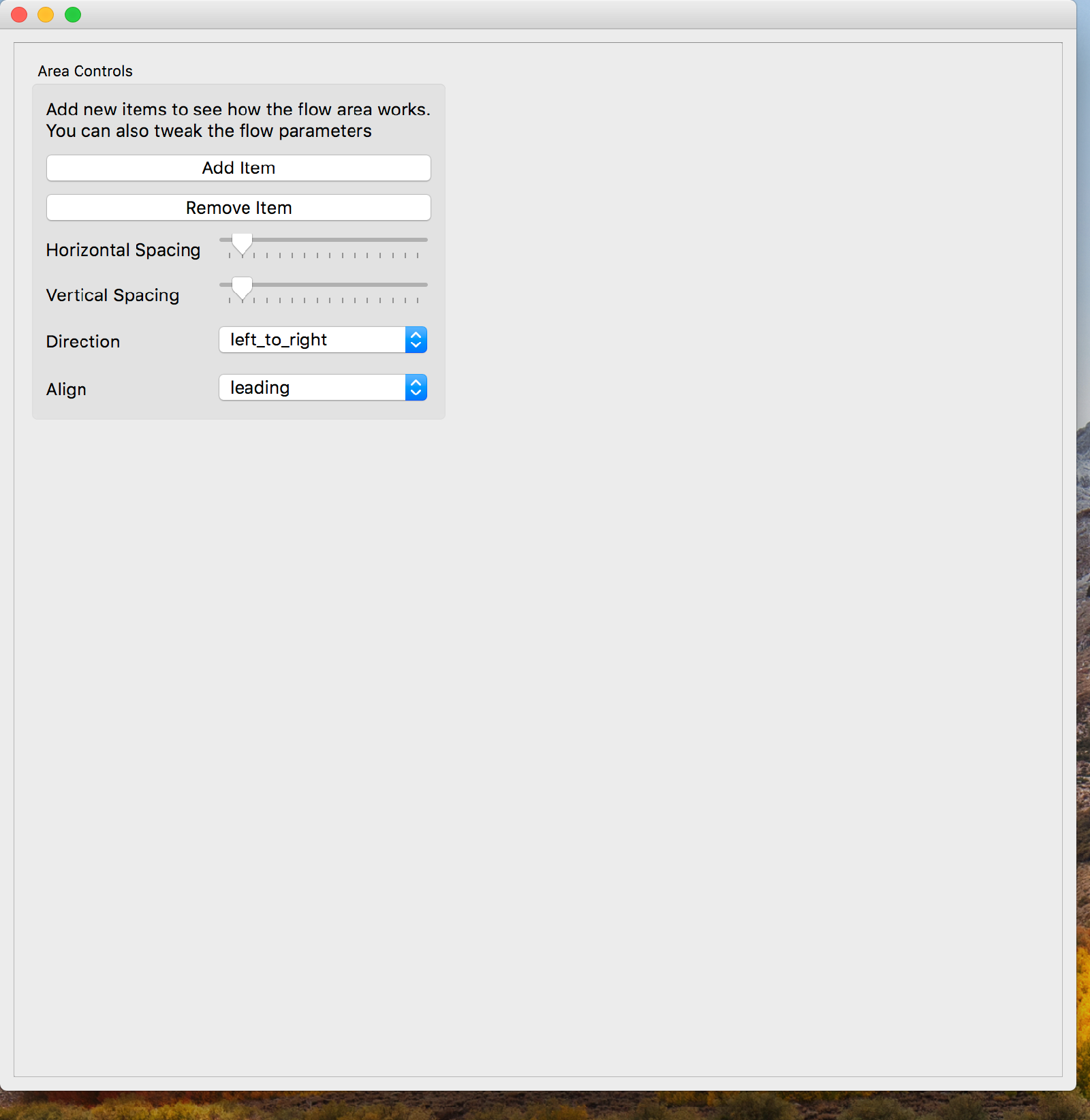
Screenshot
Example Enaml Code
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copyright (c) 2013, Nucleic Development Team.
#
# Distributed under the terms of the Modified BSD License.
#
# The full license is in the file LICENSE, distributed with this software.
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
""" An example of the `FlowArea` widget.
A `FlowArea` is a very powerful tool for creating a flowing layout of
widgets. A `FlowArea` accepts an arbitrary number of `FlowItem` children,
each of which holds a `Container` as its content. The layout of these
`FlowItem` children is controlled by the `FlowArea` attributes:
`direction`
This is an enum controlling how the items are arranged in the
area. Allowable values are 'left_to_right', 'right_to_left',
'top_to_bottom', and 'bottom_to_top'; and indicate the direction
in which items will be added to the area. When the layout space
in a given direction is exhausted, the layout will wrap around
to the next line. With horizontal directions, lines are stacked
top to bottom. With vertical directions, lines are stacked
left to right.
`align`
This is an enum controlling how a layout line is aligned within
the layout space. If there is any space leftover after laying
out a given line of widgets, that space is distributed according
to the value of this enum. Allowable values are 'leading',
'trailing', 'center', and 'justify'.
`horizontal_spacing`
This is an int specifying how much horizontal space to place
between items or lines in the layout.
`vertical_spacing`
This is an int specifying how much vertical space to place
between items or lines in the layout.
`margins`
This is a Box of ints specifying how much margin to place
on the outside of the layout.
Each `FlowItem` used in the layout can further customize the behavior:
`preferred_size`
This is a Size specifying the desired layout size for the item.
This size will be used whenever possible, but will not override
the minimum or maximum size of the item. If set to (-1, -1)
(the default), then the size hint for the item will be used.
`align`
This is an enum which controls the orthogonal alignment of the
item. When an item has neighbors which are larger than itself
in the orhthongonal direction, this value controls how the item
aligns within that additional space. The valid values area
'leading', 'trailing', and 'center'.
`stretch`
This is an int which controls the amount that the widget should
expand to take up additional space in the layout direction. The
default is 0 and means that the widget will not expand. When the
value is greater than zero, the value is weighted against the
stretch factors of the other items in the same line to determine
the amount of space given to the item.
`ortho_stretch`
This is an int which controls the amount that the widget should
expand to take up additional space orthogonal to the layout
direction. The default is 0 and means that the widget will not
expand. If no item in a given line can expand in the ortho
direction, then the line will not expand. Otherwise, the stretch
factor for a line is equivalent to the maximum of the ortho
stretch factors for all items in the line. The extra orthogonal
space is then proportioned to the lines weighted on this stretch
factor.
The code below creates a flow area populated with several initial flow
items. Items can be added and removed, and each individual item is
configurable. There is a single item which cannot be removed, and which
controls the parameters for the entire area.
<< autodoc-me >>
"""
from enaml.core.api import Include
from enaml.widgets.api import (
FlowArea, FlowItem, Window, Form, Label, Field, SpinBox, ComboBox,
Container, Html, GroupBox, Slider, PushButton,
)
enamldef Item(FlowItem):
align << align_box.selected_item
stretch << flow_spin.value
ortho_stretch << ortho_spin.value
preferred_size << (pref_width.value, pref_height.value)
GroupBox:
Form:
padding = 0
Label:
text = 'Preferred Width'
SpinBox: pref_width:
minimum = -1
maximum = 800
value = -1
Label:
text = 'Preferred Height'
SpinBox: pref_height:
minimum = -1
maximum = 800
value = -1
Label:
text = 'Flow Stretch'
SpinBox: flow_spin:
minimum = 0
maximum = 100
value = 0
Label:
text = 'Ortho Stretch'
SpinBox: ortho_spin:
minimum = 0
maximum = 100
value = 0
Label:
text = 'Ortho Align'
ComboBox: align_box:
items = ['leading', 'center', 'trailing']
index = 0
Html:
source = '<center>Hello World</center>'
enamldef AreaControls(GroupBox):
attr area: FlowArea
event add_item
event remove_item
title = 'Area Controls'
Label:
text =('Add new items to see how the flow area works.\n'
'You can also tweak the flow parameters')
PushButton:
text = 'Add Item'
clicked :: add_item()
PushButton:
text = 'Remove Item'
clicked :: remove_item()
Form:
padding = 0
Label:
text = 'Horizontal Spacing'
Slider:
minimum = 0
maximum = 150
value := area.horizontal_spacing
Label:
text = 'Vertical Spacing'
Slider:
minimum = 0
maximum = 150
value := area.vertical_spacing
Label:
text = 'Direction'
ComboBox:
items = [
'left_to_right', 'right_to_left',
'top_to_bottom', 'bottom_to_top',
]
index = items.index(area.direction)
selected_item >> area.direction
Label:
text = 'Align'
ComboBox:
items = ['leading', 'center', 'justify', 'trailing']
index = items.index(area.align)
selected_item >> area.align
enamldef Main(Window):
initial_size = (800,800)
Container:
FlowArea: flow_area:
FlowItem:
AreaControls:
area = flow_area
add_item ::
inc.objects.append(Item())
remove_item ::
if inc.objects:
inc.objects.pop()
Include: inc:
pass